
Intoeing means that while walking, the child’s the feet turn inward instead of pointing straight ahead. This is usually noticed by the parents when the baby starts to walk, but can occurs at different ages of childhood. In severe cases, intoing may cause the child to trip and fall as the toes strike the opposite heel.
Most children with intoing under the age of 8 years old, will correct spontaneously without treatment. However, children with intoeing who also have pain, swelling or limping, should be seen by a doctor.
There are three forms of intoing according to the location of the deformity:
The feet (metatarsus adductus):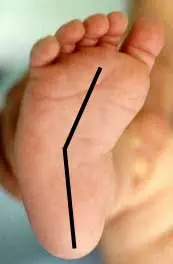
The front of the foot is curved inwards in relation to the rest of the foot. Usually the metatarsus adductus corrects without treatment. But if the feet are not flexible and the problem does not seem to be getting better plaster casts or minor surgery may be used to correct the deformity.
The shin bone – internal tibial torsion
Intoeing may be due to inward twisting of the shin bone (also known as internal tibial torsion). This becomes noticeable when your child begins walking. Its medical name is internal tibial torsion. This usually corrects with normal growth by the age of five years.
The thigh bone– femoral anteversion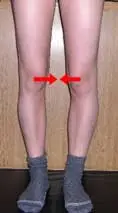
There is internal twisting of the thigh bone (femur) causing the whole leg to turn inward. It is more common in children between the ages of three to six years. It usually corrects with normal growth by the age of 14 years.

